热带条件下多年生黑麦草水分胁迫阈值及Ks系数评估
Pessl植物生理生态系统:热带条件下多年生黑麦草水分胁迫阈值及Ks系数评估
Pessl植物生理生态监测系统的全套监测系统和在线平台FieldClimate适用于所有气候区,可用于各种行业和各种用途——从农业到研究、水文、气象、洪水警报等。iMetos植物生理生态监测系统已经成为一个全球品牌,使用持续时间更长,性能更好,是通用的天气监测设备,具有早期识别和警报功能(有SMS手机提醒功能);可以用来计划、控制和管理复杂的独立气象过程。该监测系统专为不同气候区域的多种任务而设计。其可以安装多达600个传感器,如土壤和空气湿度、温度、降雨、风速、风向、叶片 湿度、总体辐射等传感器。

摘要:多年生黑麦草(Lolium perenne) 是哥伦比亚赤道高地地区的主要牧草作物,因为它具有很高的营养价值和生产牛奶和肉。本研究旨在确定可用土壤水分的相对消耗与多年生黑麦草冠层扩张和关闭气孔的Ks值之间的关系,并确定水分胁迫的阈值。实验在受控环境条件下的盆中进行。这些花盆以完全随机的方式排列。该实验包括五种处理——包括对照处理——土壤水分亏缺的处理,随着作物周期的发展,这些处理逐渐增加了枯竭水平。这产生了一个生长阶段的各种条件。对于每个处理,进行四次重复 生物质生产受到水分胁迫的显着影响。结果表明,Ks 的上限和下限分别为冠层扩张(CE)的土壤中总有效水(TAW)耗竭水平(p)的 0.28 和 1.3,以及 0.25 和 1.1p TAW 气孔关闭 (gs)。二次函数适用于 CE (R2 = 0.72) 和 CS (R2 = 0.73);此外,具有正形状因子(sf)的FAO-AquaCrop的Ks函数如下:sf = 11,CE为0.22,sf = 4.3,gs为RMSE 0.19。我们的研究结果表明,黑麦草对水分胁迫具有中等敏感性。粮农组织的 Ks 函数与实验数据之间发现的差异要求使用模型,并根据每个案例调整参数。
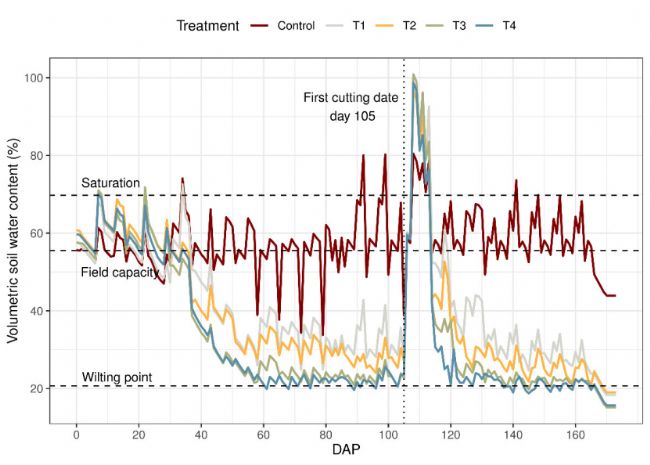
试验期间不同处理的土壤体积含水量(%) 与种植后天数的关系
Water Stress Thresholds and Evaluation of Coefficient Ks for Perennial Ryegrass in Tropical Conditions
Abstract: Perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) is the predominant forage crop in the equatorial highland zones of Colombia due to its high nutritional value and versatility to produce both milk and meat. This study aimed to determine the relationship between the relative depletion of usable soil water and the Ks values of canopy expansion and closure stomatal of perennial ryegrass, as well as to identify the threshold values of water stress. The experiment was carried out in pots under a controlled environment condition. These pots were arranged in a completely randomized manner. The experiment consisted of five treatments—including control treatment—of water deficits in the soil that progressively increased the depletion level as the crop cycle developed. This generated a wide range of conditions in the growth stages. For each treatment, four repetitions were performed Biomass production was significantly affected by water stress. The results show that the upper and lower thresholds of Ks were 0.28 and 1.3 of the depletion level (p) of the total available water (TAW) in the soil for the expansion of the canopy (CE), and 0.25 and 1.1 p of the TAW for stomatal closure (gs). Quadratic functions were fitted for both the CE (R2 = 0.72) and CS (R2 = 0.73); moreover, the
Ks function of FAO-AquaCrop with positive shape factor (sf) was as follows: sf = 11, RMSE 0.22 for CE, and sf = 4.3, RMSE 0.19 for gs. Our results indicate that ryegrass is moderately sensitive to water stress. The differences found between the Ks function of FAO and the experimental data call for the need to use modeling with parameters adapted for each case.





