组织透明化在神经科学领域中的应用
神经科学是一门神秘的科学,也一直是生命科学研究的热点。如果有一天,我们可以搞明白神经细胞是怎么一回事,神经细胞之间是如何协作的,或许我们就能明白意识是如何产生的了?明白了我们为什么要睡觉?明白了男人和女人的大脑有什么不一样?为了明确神经元的结构和功能连接,需要对整个大脑和脊髓中的神经元及突触进行成像和追踪。组织透明化技术的发展使生物样本变得透明,为生物组织结构的三维可视化研究打开了大门,并为进一步探索人类疾病的复杂性提供了崭新的平台,近年来组织透明化技术在生物医学研究领域得到了广泛应用。
BRADKE等利用3DISCO透明化技术和光片显微镜成像技术识别、追踪和评估脊髓损伤后的轴突再生,确定了轴突再生能力及再生轴突轨迹,有助于解释轴突再生机制,同时定量测定了脊髓损伤后神经胶质的活动反应。
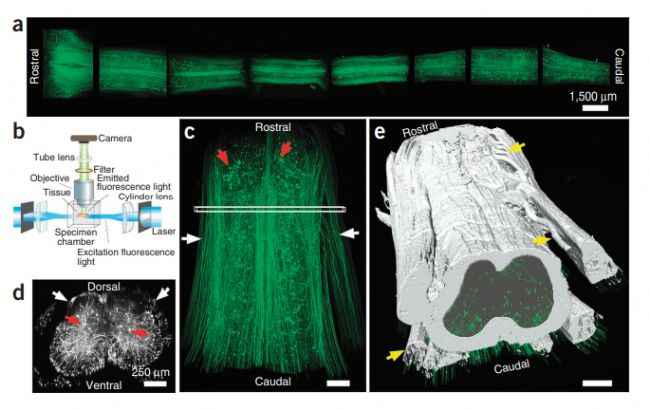
Imaging large regions of the spinal cord of GFP-M mice
(a) Entire spinal cord of a GFP-M mouse cut into 3- to 4-mm-long segments, cleared and imaged with ultramicroscopy. (b) Drawing of the ultramicroscopy setup showing tissue positioning and the light path. (c) A spinal cord segment (length 4 mm, T12 to L2 spine level) of a GFP-M mouse scanned with ultramicroscopy shown in a horizontal view. (d) Cross-view projection (50-µm thickness) of the indicated region in c. White arrows in c,d mark individual axons in the white matter; red arrows mark cell bodies in the gray matter. (e) Traced white and gray matter boundaries and axon bundles (yellow arrows).
阿尔兹海默症(AD)是一种起病隐匿的进行性发展的神经系统退行性疾病。临床上以记忆障碍、失语、失用、失认、视空间技能损坏、执行功能障碍以及人格和行为改变等全面性痴呆表现为特征,细胞外β淀粉样蛋白沉积和细胞内tau蛋白磷酸化是AD的主要病理特征。Liebmann等人利用iDISCO技术对阿尔兹海默症模型小鼠脑进行透明化阐明了β淀粉样蛋白沉积和小胶质细胞及脉管系统之间的空间分布关系,这将对阿尔兹海默症的科学研究和治疗产生重大意义。
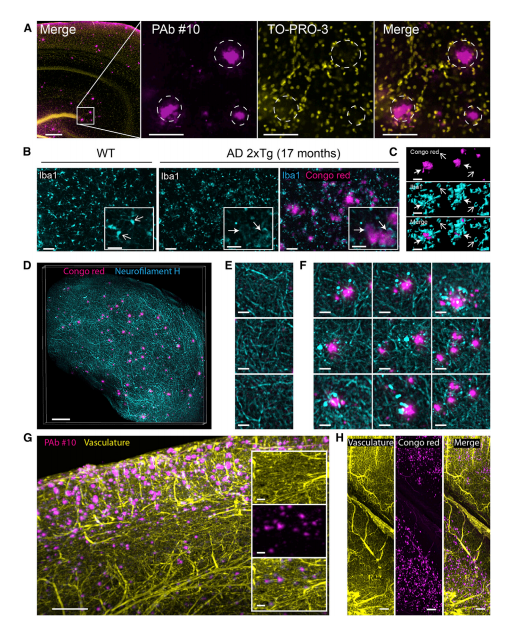
Double Labeling of β-Amyloid Plaques and Reactive Microgliosis, Axonal Dystrophy, or Vasculature in Cleared AD Brains with Volume Imaging
(A)confocal image of β-amyloid plaques and cell nuclei double staining in a 17-month-old2xTg AD cleared mouse brain. (B) Confocal optical slices of microglia stained with anti-Iba1 antibody. (C) 3D surface rendering of four isolated β-amyloid plaques and neighboring microglia cells from the AD brain described in (B). (D)Maximum intensity projection of β-amyloid plaques and neuro filament H staining in a10-month-old 2xTgAD cleared mouse cortex(500mmthick). (E)Magnified region from (D) showing labeled axons in absence of β-amyloid plaques. (F) Magnified region from (D) showing dystrophic axons surrounding labeled β-amyloid plaques. (G) Maximum intensity projection of optical section (1mm) from the cortex of an 11-month-old 2xTgAD mouse brain labeled for plaques (anti-b amyloid anti-bodies) and vasculature. (H)Maximum intensity projection of optical section (1mm) from the cortex and hippocampus of an 8-month-old 2xTgAD mouse brain labeled for plaques (Congored) and vasculature.
Chung等人通过CLARITY技术获得透明而完整的小鼠大脑,利用Thy1–eYFP信号实现了对小鼠大脑神经元进行远距离投射、神经回路、细胞关系、亚细胞结构、蛋白质复合物、 核酸和神经递质的成像。展现了大脑中复杂的精细连接和分子结构。

Intact adult mouse brain imaging
a, Cajal quote before CLARITY. b, Cajal quote after CLARITY: Thy1–eYFP line-H mouse brain after hydrogel–tissue hybridization, ETC and refractive-index matching. c, Fluorescence image of brain depicted in b. d, Dorsal aspect is imaged, then brain is inverted and ventral aspect imaged. e, Three-dimensional rendering of clarified brain imaged;f, Non sectioned mouse brain tissue showing cortex, hippocampus and thalamus;g–l, Optical sections from f showing negligible resolution;m, Cross-section of axons in clarified Thy1–channelrhodopsin2 (ChR2)–eYFP striatum;n, Dendrites and spines of neurons in clarified Thy1–eYFP line-H cortex.
MURAKAMI等人应用CUBIC-X透明并膨大小鼠大脑,在亚细胞水平对整个小鼠大脑进行成像,并绘制出了一张小鼠大脑图谱。他们采用化学方法标记了大脑中的每个细胞,然后在大脑透明化的同时将其尺寸扩大了十倍,利用精密成像技术对神经元进行了三维重建,总计约7200万个细胞。
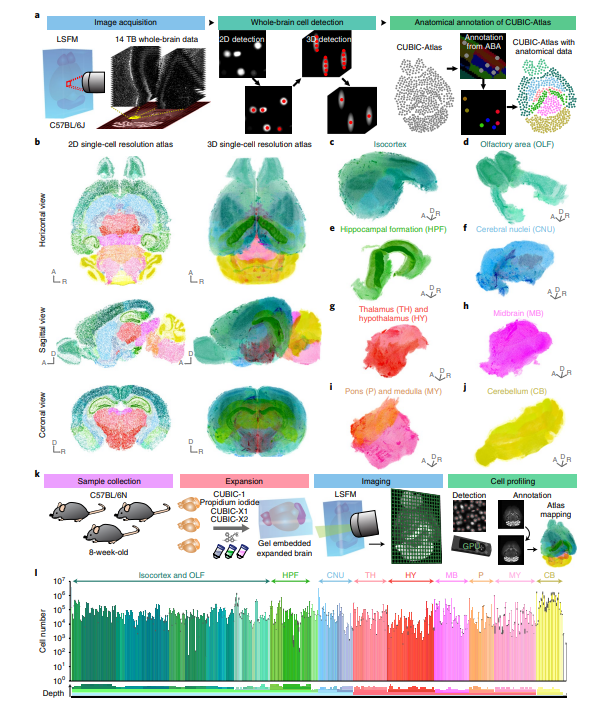
Construction of a single-cell-resolution mouse brain atlas (CUBIC-Atlas)
a, Overview of construction of the CUBIC-Atlas. b, The CUBIC-Atlas. Horizontal, sagittal and coronal view of single-plane images (left) and volume-rendered images (right) of the CUBIC-Atlas. c–j, Major anatomical areas in the CUBIC-Atlas. k, Overview of whole-brain cell counting in C57BL/6N 8-week-old male mice. l, Cell numbers in each brain area.
目前组织透明化方法有油性,基于水凝胶和水性的组织透明化方法。其中油性组织透明化方法主要有BABB, 3DISCO, uDISCO,FDISCO和 PEGASOS等,基于水凝胶的透明化方法有CLARITY和SHIELD,水性组织透明化方法有CLearT/CLearT2,SeeDB, FRUIT, Scale和CUBIC等方法。而锘海研发的透明化试剂盒依托测样服务中积累到的丰富而宝贵的经验,对各种透明化方法进行测试和比较后对试剂配方进行了精心优化,使其在组织荧光保护、样本形态维持、降低自发荧光等方面表现出非常优异的性能,是研究神经科学的不二之选。
锘海组织透明化试剂盒
参考文献:
1. Ertürk A, Mauch CP, Hellal F, Förstner F, Keck T, Becker K, Jährling N, Steffens H, Richter M, Hübener M, Kramer E, Kirchhoff F, Dodt HU, Bradke F. Three-dimensional imaging of the unsectioned adult spinal cord to assess axon regeneration and glial responses after injury. Nat Med. 2011 Dec 25;18(1):166-71. doi: 10.1038/nm.2600. PMID: 22198277.2. Liebmann T, Renier N, Bettayeb K, Greengard P, Tessier-Lavigne M, Flajolet M. Three-Dimensional Study of Alzheimer's Disease Hallmarks Using the iDISCO Clearing Method. Cell Rep. 2016 Jul 26;16(4):1138-1152. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.060. Epub 2016 Jul 14. PMID: 27425620; PMCID: PMC5040352.
3. Chung K, Wallace J, Kim SY, Kalyanasundaram S, Andalman AS, Davidson TJ, Mirzabekov JJ, Zalocusky KA, Mattis J, Denisin AK, Pak S, Bernstein H, Ramakrishnan C, Grosenick L, Gradinaru V, Deisseroth K. Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature. 2013 May 16;497(7449):332-7. doi: 10.1038/nature12107. Epub 2013 Apr 10. PMID: 23575631; PMCID: PMC4092167.
4. Murakami TC, Mano T, Saikawa S, Horiguchi SA, Shigeta D, Baba K, Sekiya H, Shimizu Y, Tanaka KF, Kiyonari H, Iino M, Mochizuki H, Tainaka K, Ueda HR. A three-dimensional single-cell-resolution whole-brain atlas using CUBIC-X expansion microscopy and tissue clearing. Nat Neurosci. 2018 Apr;21(4):625-637. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0109-1. Epub 2018 Mar 5. PMID: 29507408.
5. Tian T, Yang Z, Li X. Tissue clearing technique: Recent progress and biomedical applications. J Anat. 2021 Feb;238(2):489-507. doi: 10.1111/joa.13309. Epub 2020 Sep 16. PMID: 32939792; PMCID: PMC7812135.
锘海生命科学为广大客户提供专业的生物组织透明化、免疫染色、平铺光片显微镜3D荧光成像、数据分析、数据存储等一站式科研服务,旨在通过快速、多样化的科研服务为每一位生命科学工作者提供个体化/定制化的解决方案。

了解更多组织透明化染色、3D荧光成像等相关信息





