病毒免疫逃逸机制--诱导免疫细胞凋亡、衰老和耗竭
前言
病毒选择宿主的初衷是为了寄生,复制自己,所以它会进化以逃逸人体免疫系统,达到长久寄生以及在人际间传播的目的。
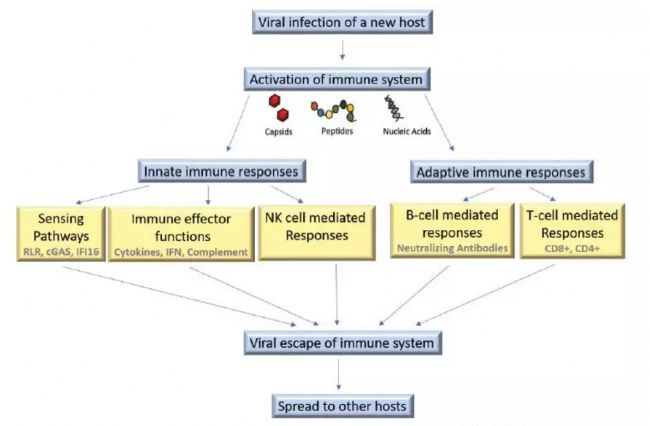
COVID-19病人临床资料,ICU重症病人,淋巴细胞计数远低于Non-ICU病人,提示病毒可能通过某些机制引起了淋巴细胞的减少。
恒瑞等启动了免疫检查点抑制剂新冠肺炎的临床。众所周知免疫检查点参与T细胞耗竭。
基于此,想谈谈免疫细胞凋亡,衰老,耗竭在病毒感染逃逸中的作用。
对于新冠肺炎病毒,现在并无明确定论的研究,不做讨论,避免产生误导。
以HCV为例来写本文。
HCV感染与诱导免疫细胞及肝细胞凋亡
HCV于1989年首次被确定为丙型肝炎感染的病原体,是一种属于Flaviviridae病毒科Hepacivirus属的RNA病毒。
越来越多的证据表明,病毒倾向于利用宿主细胞机制诱导组织或免疫细胞凋亡,作为延缓病毒特异性免疫反应,最终导致持续感染的一种途径。
一般来说,病毒利用死亡受体和非受体信号通路。
在受感染个体的细胞表面诱导促凋亡受体或其配体,作为诱导细胞死亡的手段,并最终持久化感染。在慢性HCV感染过程中,肝细胞通过上调死亡诱导配体CD95/FAS、TNF相关凋亡诱导配体(TRAIL)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α),诱导细胞凋亡。
另一项研究认为,某些HCV结构蛋白可以作为免疫调节剂,在肝细胞上上调FASL,使激活的外周T细胞通过caspase3激活发生凋亡,最终抑制抗病毒反应,以协助病毒的持久性感染。
HCV特异性CD8T细胞的丢失,可能会延缓HCV感染细胞的消除和病毒中和。
同时,HCV也通过非受体介导的线粒体凋亡途径。即caspase3的激活、活化caspase3的核易位、ROS的分泌和线粒体细胞色素c的释放。
免疫衰老(Immunosenescence)
在正常的人类衰老过程中,宿主免疫系统在对外来抗原的细胞反应方面的功能变得很差,导致幼稚的T细胞替换不良,并通过一系列称为免疫衰老的事件增加衰老表型T细胞的扩张。在正常衰老过程中,T细胞变得越来越容易受到免疫衰老的影响,从而导致功能幼稚T细胞库频率低下,幼稚T细胞向终末分化T细胞分化率增加,端粒缩短,CD4/CD8比值下降,缺乏CD28共刺激分子的记忆T细胞数量增加,导致感染、自身免疫性疾病、慢性炎症性疾病和癌症易感率增加。
已经证明某些慢性病毒感染,特别是HIV和HBV,通过一个被称为复制性衰老的过程,在免疫损伤方面起着明确的作用。机制是由于T细胞持续暴露于病毒蛋白导致慢性免疫激活(CIA),复制衰老的T细胞通常表现为共刺激分子(CD28和CD27)以及T细胞存活分子(CD127)表达水平较低。这些细胞一起也增加了CD57的表达,CD57是复制衰老的生物标记物,以及CD38和HLA-DR等慢性激活标记物的过度表达。
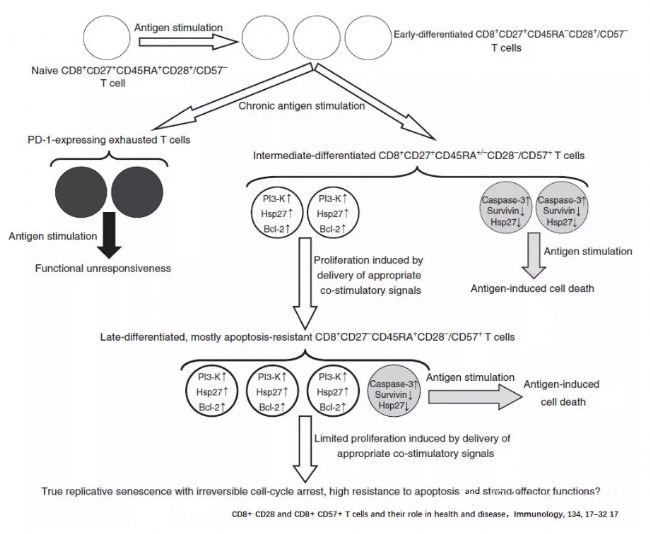
慢性HCV感染的患者中也观察到了类似的现象,在这些患者中,出现了更高比例的效应衰老CD8+CD57+T细胞,这在肝硬化中似乎也明显更高。
免疫耗竭(Immune Exhaustion)
在病毒感染过程中,抗原提呈细胞(APC),如树突状细胞,将病毒衍生的肽抗原呈递给幼稚的CD4T细胞,进而产生IL-2、IFN-γ和TNF-α激活。这有助于短命的细胞毒性T淋巴细胞(CTLs)分化为记忆细胞和效应细胞CD8T细胞,最终通过分泌穿孔素和颗粒酶杀死病毒感染的细胞。
然而,有一种完全相反的现象称为T细胞衰竭,即在一些病毒感染的患者中,T细胞亚群的功能将受到损害,同时导致慢性炎症状态以及重复刺激T细胞。
CD8和CD4T细胞衰竭的另一个重要标志是抑制分子/阴性免疫检查点的上调,在感染腺病毒、HIV、HBV和HCV时,这些检查点与APCs上表达的同源配体结合。
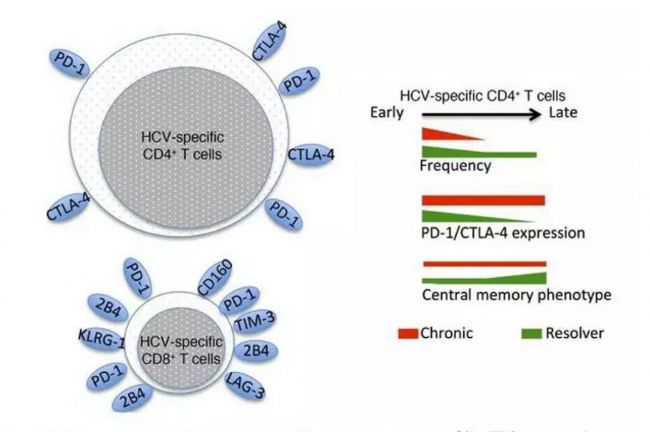
研究表明,在急性感染时,PD-1在HCV特异性T细胞上的表达相对较高,并且很大一部分细胞在HCV感染的慢性阶段表达PD-1,尽管这与HCV疾病的临床结果无关。在另一项研究中,研究人员证明,肝硬化患者脾脏中的T细胞表达更高水平的PD-1和TIM-3,主要在效应记忆亚群体中表达。
PD-1可能在CD8T细胞功能障碍中起作用,导致病毒持久性感染。另一项关于慢性HCV感染中T细胞衰竭的研究表明,T细胞在急性感染后立即发生快速衰竭,连续丧失IL-2的产生、增殖和IFN-γ产生,并增加TIM-3、PD-1和CTLA-4的表达,并在此后持续较长时间。
MAIT(粘膜相关恒定细胞)的丢失是否有助于HCV的持久感染?
具有抗菌特性的特殊的、先天样的T细胞,称为粘膜相关恒定的T(MAIT)细胞,是人类进化保守的T细胞亚群,在系统循环中处于丰富的水平,占健康成人总t细胞库的1-8%。肺和肝组织中也可见MAIT细胞(约占肝脏T细胞的50%)
MAIT细胞与不变自然杀伤T细胞(INKT)具有表型相似性,表达高水平的IL-12Rβ2、IL-18Rα和CD161与半不变Vα7.2段。
这些细胞很容易被IL-12和IL-18以及一些外来抗原(微生物衍生的维生素b代谢物)刺激,它们是由单体MHC-I类相关蛋白(MR1),在共刺激分子CD80或CD86的帮助下呈现的,尽管MAIT细胞不是细胞介导的免疫反应的一部分。
激活后,MAIT细胞往往分泌广泛的细胞因子(IL-4、IL-5、IL-10、IFN-γ、TNF-α、IL-17和IL-22)或释放穿孔素以及颗粒酶,可杀死微生物感染的细胞。
最近的研究表明,虽然MAIT细胞对病毒感染起着关键作用,但它们不能直接识别病毒感染的细胞。然而,从感染细胞中释放出的几种先天细胞因子(IL-18、IL-12、IL-15和IFN-)对MAIT细胞有刺激作用,研究人员已经表明,MAIT细胞在慢性HCV感染过程中严重减少,并出现耗竭和衰老表型。慢性HCV患者的MAIT细胞除了PD-1、CD38和HLA-DR外,还表达高水平的CD57。
推测,在慢性HCV感染过程中,由于细胞的反复激活而导致外周MAIT细胞衰竭和衰老,可能导致先天防御属性减弱,从而导致病毒的持久性和HCV疾病的进展。
自然界很多规律或有相通之处。
参考文献
-
Chaolin Huang et al, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The lancet,Available online 24 January 2020
-
Iannello, A.; Debbeche, O.; Martin, E.; Attalah, L.H.; Samarani, S.; Ahmad, A. Viral strategies for evading antiviral cellular immune responses of the host. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 16–35.
-
Iannello, A.; Debbeche, O.; Martin, E.; Attalah, L.H.; Samarani, S.; Ahmad, A. Viral strategies for evading antiviral cellular immune responses of the host. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 16–35.
-
Iken, K.; Huang, L.; Bekele, H.; Schmidt, E.V.; Koziel, M.J. Apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is enhanced by co-culture with hepatocytes expressing hepatitis C virus (HCV) structural proteins through FasL induction. Virology 2006, 346, 363–372
-
Barathan, M.; Gopal, K.; Mohamed, R.; Ellegård, R.; Saeidi, A.; Vadivelu, J.; Ansari, A.W.; Rothan, H.A.; Ravishankar Ram, M.; Zandi, K.; et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection triggers spontaneous differential expression of biosignatures associated with T cell exhaustion and apoptosis signaling in peripheral blood mononucleocytes. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 466–480
-
Saeidi, A.; Chong, Y.K.; Yong, Y.K.; Tan, H.Y.; Barathan, M.; Rajarajeswaran, J.; Sabet, N.S.; Sekaran, S.D.; Ponnampalavanar, S.; Che, K.F.; et al. Concurrent loss of co-stimulatory molecules and functional cytokine secretion attributes leads to proliferative senescence of CD8+ T cells in HIV/TB co-infection. Cell. Immunol.2015, 297, 19–32
-
Bucks, C.M.; Norton, J.A.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Mueller, Y.M.; Katsikis, P.D. Chronic antigen stimulation alone is sufficient to drive CD8+ T cell exhaustion. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6697–6708
-
Viral evolution and Immune responses,J Clin Microbiol Biochem Technol 5(2): 013-018
-
Raziorrouh, B.; Ulsenheimer, A.; Schraut,W.; Heeg, M.; Kurktschiev, P.; Zachoval, R.; Jung, M.C.; Thimme, R.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Horster, S.; et al. Inhibitory molecules that regulate expansion and restoration of HCV-specific CD4+ T cells in patients with chronic infection. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1422–1431.
-
CD8+ CD28 and CD8+ CD57+ T cells and their role in health and disease,Immunology, 134, 17–32 17
-
Diana Y. Chen, David Wolski,Jasneet Aneja,Lyndon Matsubara, Brandon Robilotti, Garrett Hauck, Paulo Sergio Fonseca de Sousa, Sonu Subudhi, Carlos Augusto Fernandes,Ruben C. Hoogeveen,Arthur Y. Kim, Lia Lewis-Ximenez, and Georg M. Lauer,Hepatitis C virus–specific CD4+ T cell phenotype and function in different infection outcomes ,J Clin Invest. 2020;130(2):768–773.





