慢性肾病中的隐匿杀手Alport综合征的介绍及其相关动物模型的应用
慢性肾脏疾病的种类非常丰富,但其中有一种慢性肾病可能在儿童阶段就开始显露端倪,但早期症状不明显,常常被家长忽视或被医生误诊,导致病情延误,并且这种疾病也会遗传,发展到肾衰竭的风险较高,最后只能通过透析和肾移植的方式来维持生命。这种常被称为肾病中的隐匿杀手的慢性肾病就是Alport综合征。
Alport综合征概述
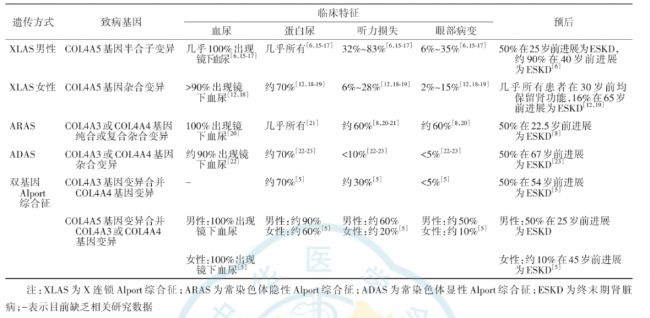
Alport综合征是一种临床表现以血尿、蛋白尿、进行性肾功能减退为特征,部分患者合并感音神经性耳聋、眼部病变等肾外表现的综合征,所以又称眼-耳-肾综合征。由于缺乏大样本流行病学数据,目前该疾病的国内发病率尚不清楚。据美国报告,Alport 综合征的基因频率为 1/10 000~1/5000。男性和女性的发病率及病情轻重与突变基因类型有关。X 连锁遗传者男女均可发病,但男性发病率高于女性,且病情较女性重。
Alport综合征致病原因
该病是由编码Ⅳ型胶原α3、α4、α5链的COL4A3、COL4A4和COL4A5基因突变导致。α3、α4、α5链形成三螺旋结构,与其他三螺旋紧密结合形成肾小球基底膜(GBM)。COL4A5 基因具有一个致病性突变或COL4A3 或者COL4A4基因具有两个致病性突变,会导致高度有序的GBM逐渐分解,这种变化加速了肾小球硬化,进而导致肾功能不全。
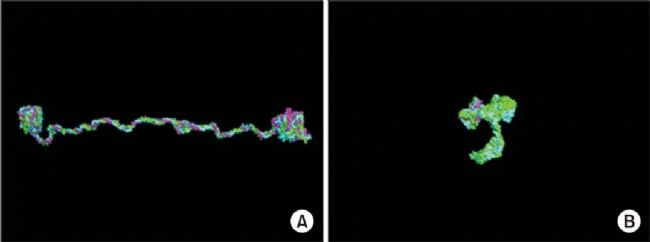
图1 A. 正常Ⅳ型胶原三螺旋结构;B. COL4A5无义突变的胶原三螺旋结构[1]
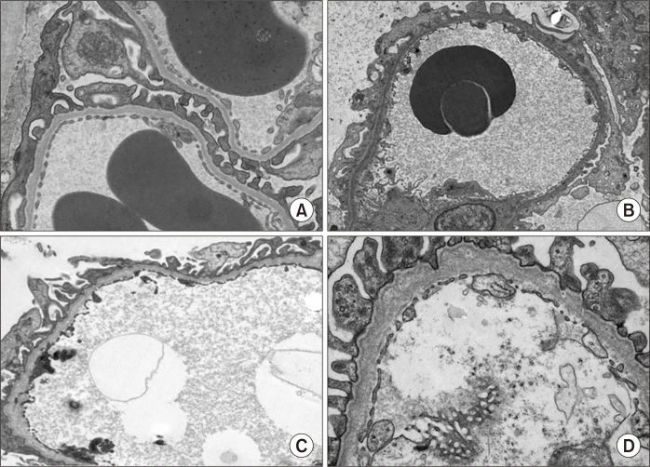
图2 A正常GBM;B-D为Alport综合征患者GBM(轻-重症)[1]
Alport综合征药物情况
目前,针对Alport综合征尚无根治或者病因性治疗措施。治疗策略旨在通过早期药物治疗延缓疾病的进展,从而延缓末期肾脏病(ESKD)的发生,否则需进行肾脏替代治疗。
《Alport综合征诊治专家共识(2023版)》中指出,肾素-血管紧张素醛固酮系统(RAAS)阻断剂是目前延缓Alport综合征肾脏疾病进展的首要推荐药物。
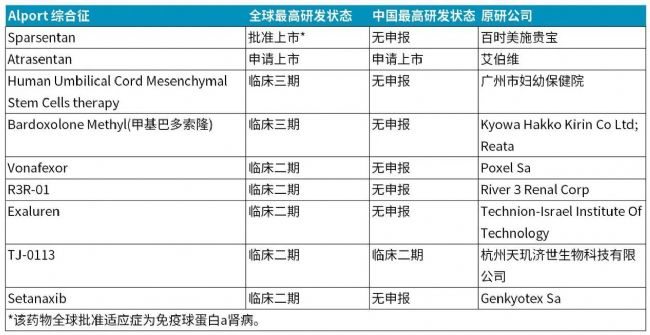
目前关于Alport综合征的药物研发进展如下表,暂无针对该适应症的获批药物。
Alport综合征相关动物模型
2019年,日本实验室构建了X连锁的Alport疾病模型,用同源重组的方法引入人类相应突变(R471X)构建了COL4A5无义突变的小鼠,使该蛋白无法正常表达。对尿液的检测发现R471X小鼠的蛋白和肌酐水平显著高于正常组;血液中总蛋白没有显著差异,但是血液中的尿氮和尿肌酐出现明显的提升。对6周大的小鼠进行免疫组实验化也发现了R471X小鼠的肾小管纤维化。
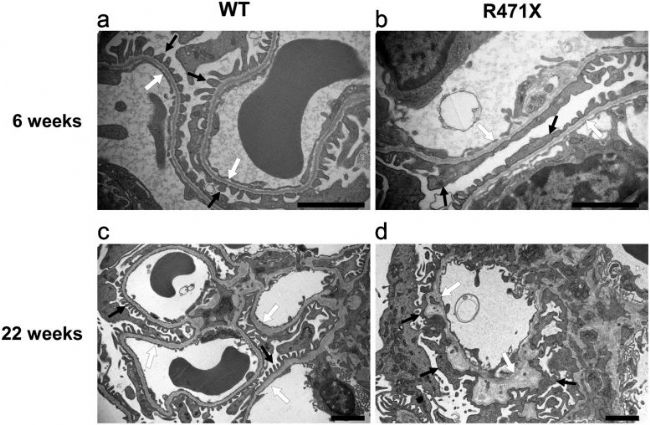
图3. 野生型和突变型(R471X)雄性小鼠肾小球基底膜。[3]
次年,针对构建的Alport疾病模型,该实验室人员使用ASO(反义寡核苷酸)疗法诱导COL4A5基因中的外显子跳跃,从而形成正常的胶原蛋白三聚体,延缓肾衰竭的进展。该研究在动物模型上展现出较好的效果,为未来Alport综合征的药物开发提供了新的思路。
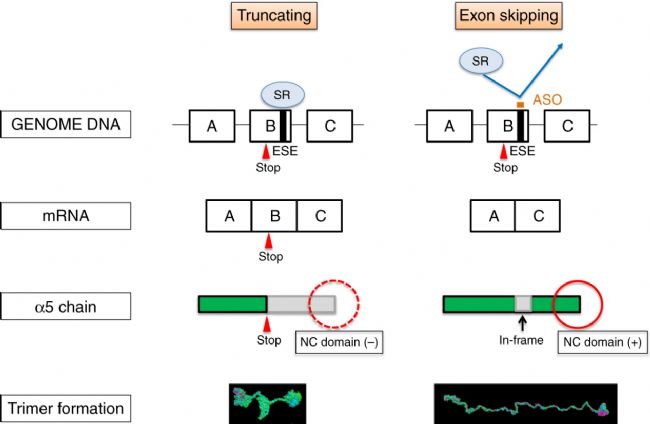
图4. 反义寡核苷酸(ASO)疗法挽救 XLAS 动物免于发生 ESRD 示意图。[4]
南模生物相关动物模型
罕见病是全人类共同面临的公共健康问题。作为一家专注于模式生物领域的公司,南模生物长期助力罕见病基因治疗研究,构建了X连锁的Alport疾病模型,助力Alport疾病的的相关机制研究需求,为相关药物的药效评估和安全性评价提供了强有力的工具。具体信息见下表:
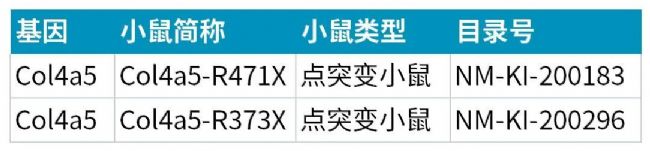
Col4A5-R471X相关验证与药效数据:
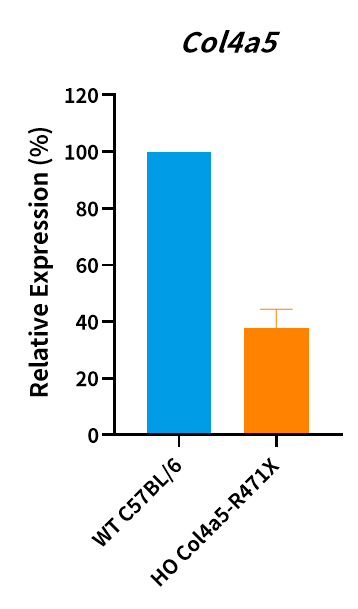
Fig.1 Col4a5 mRNA level was measured in Col4a5-R471X male mice and the point mutation of Col4a5 has been verified by sequencing (n=3, male, 7 weeks old).
Abbr. HO, homozygous; WT, wild type.
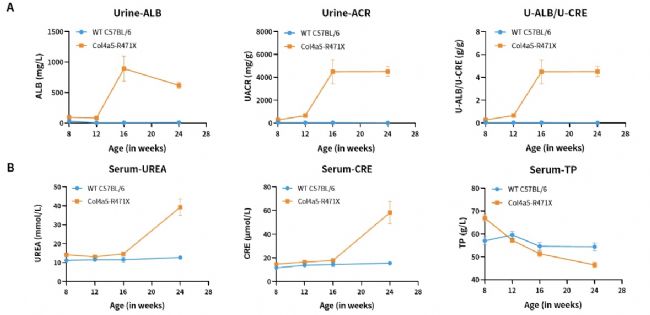
Fig.2 The results of urine (A) and blood (B) biochemical indicators in Col4a5-R471X mice (n=2 male and 6 female).
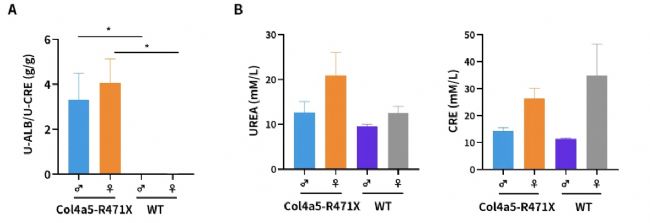
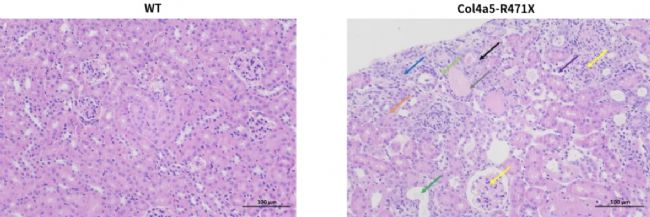
Fig.4 Marked glomerular changes are recognized in all (8/8) R471X mice of 23 weeks of age. The renal cortex shows uniform glomerular distribution, with mesangial matrix proliferation and mild sclerosis (yellow arrow). Renal tubular changes include epithelial edema (blue arrow), atrophy (orange arrow), dilation (green arrow), and necrosis (black arrow). Connective tissue proliferation (light green arrow), lymphocyte infiltration (purple arrow), and occasional protein casts (gray arrow) are noted. Such lesions are entirely absent in controls of same age. Scale bar=100 μm; magnification, 200×.
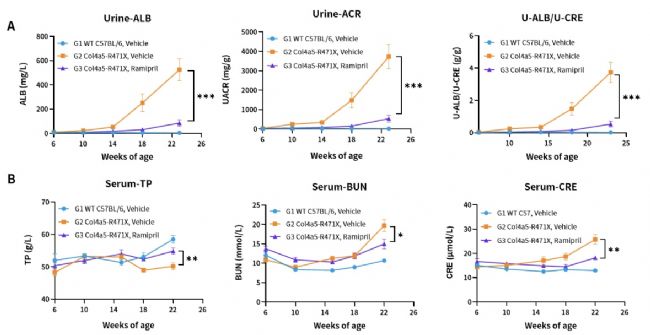

Fig.6 Effects of Ramipril (10mg/kg) on urine (A) and plasma (B) biochemical indicators of male and female Col4a5-R471X mice over a 16-17 weeks treatment period respectively (6 weeks of age at initiation time, n=4-5 male and 4-5 female in each group).

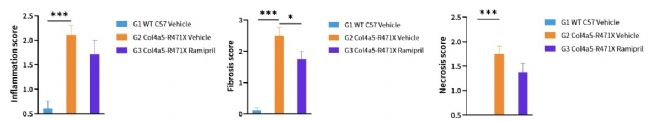
Fig.8 Histopathology changes of Col4a5-R471X mice over a 17 weeks treatment period (6 weeks of age at initiation time, n=4-5 male and 4-5 female in each group). Data are presented as mean and ± SEM
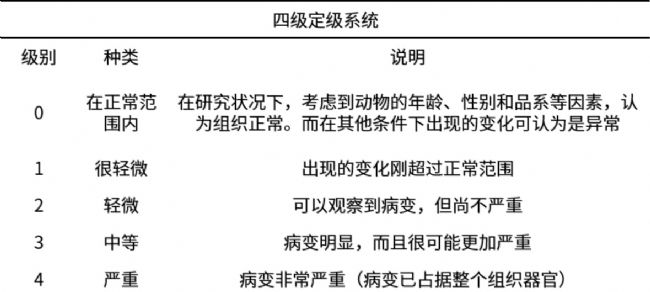
附:病理评价标准[5]
[1]Nozu K, Takaoka Y, Kai H, et al. Genetic background, recent advances in molecular biology, and development of novel therapy in Alport syndrome. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2020;39(4):402-413. doi:10.23876/j.krcp.20.111
[2]https://www.cma.org.cn/?c=0
[3]Hashikami K, Asahina M, Nozu K, Iijima K, Nagata M, Takeyama M. Establishment of X-linked Alport syndrome model mice with a Col4a5 R471X mutation. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018;17:81-86. Published 2018 Dec 12. doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.12.003
[4]Yamamura, T., Horinouchi, T., Adachi, T. et al. Development of an exon skipping therapy for X-linked Alport syndrome with truncating variants in COL4A5. Nat Commun 11, 2777 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16605-x
[5]Peter. Mann 等.大鼠和小鼠病理变化术语及诊断标准的国际规范(INHAND)[M].杨利峰,周向梅,赵德明主译.北京:中国农业出版社,2019.
关于我们
上海南方模式生物科技股份有限公司(Shanghai Model Organisms Center, Inc.,简称"南模生物"),成立于2000年9月,是一家上交所科创板上市高科技生物公司(股票代码:688265),始终以编辑基因、解码生命为己任,专注于模式生物领域,打造了以基因修饰动物模型研发为核心,涵盖多物种模型构建、饲养繁育、表型分析、药物临床前评价等多个技术平台,致力于为全球高校、科研院所、制药企业等客户提供全方位、一体化的基因修饰动物模型产品解决方案。





