特应性皮炎小鼠模型的介绍及其在药物评估与科学研究中的应用
亲爱的朋友们,今天我们来聊一聊一个让许多人困扰的问题——特应性皮炎。这是一种常见的皮肤病,给患者的生活带来了不少烦恼。
下面,就让我们一起来了解一下吧!
01 什么是特应性皮炎
特应性皮炎,又称异位性皮炎、遗传过敏性皮炎,是一种具有遗传倾向的慢性皮肤病。它通常发生在儿童和青少年,但也可能在成年人中出现。特应性皮炎的发病原因复杂,可能与遗传、环境、免疫等多种因素有关。
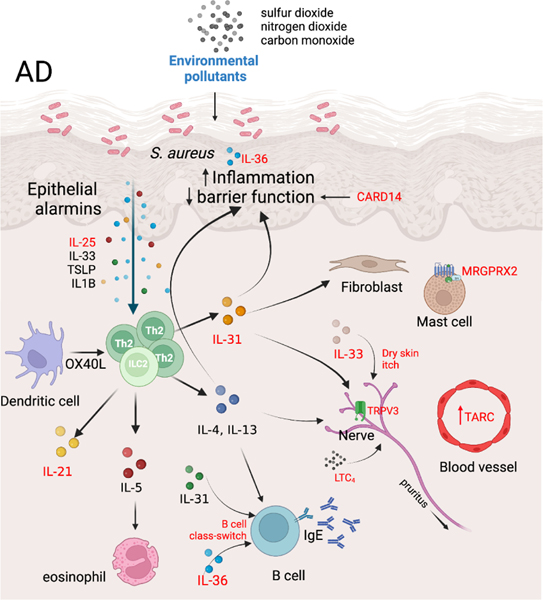
Fig1. Novel insights and additions to AD pathogenesis[1].
02 特应性皮炎的症状和特点
★ 皮肤干燥、瘙痒;
★ 红斑、肿胀;
★ 出现丘疹或水疱;
★ 严重时可伴有渗出和结痂;
★ 反复发作,病程较长。
03 特应性皮炎的治疗
药物治疗主要包括外用糖皮质激素、钙调磷酸酶抑制剂、口服抗组胺药和免疫抑制剂等;非药物治疗强调皮肤保湿和护理,避免过敏原和刺激物的接触[4-5]。
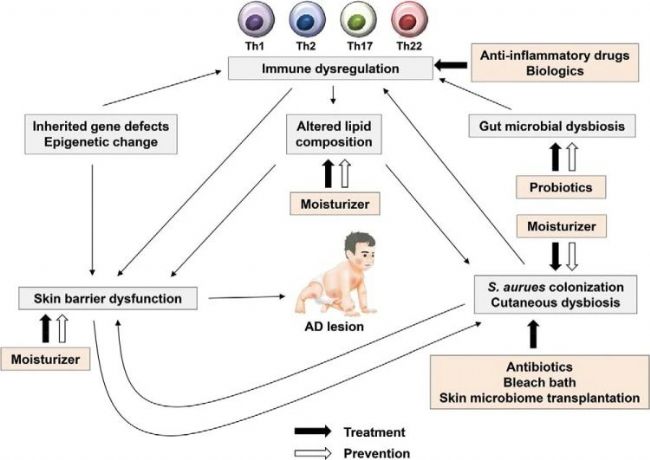 Fig2. Prevention and treatment of AD[2].
Fig2. Prevention and treatment of AD[2].
04 特应性皮炎小鼠模型的起源
特应性皮炎小鼠,是通过特定的遗传筛选和培育得到的。如C57BL/6小鼠、BALB/c小鼠,这些小鼠在特定的遗传背景下,容易出现皮肤炎症、瘙痒等症状,与人类特应性皮炎的表现相似。因此,它们成为了研究特应性皮炎的理想模型。
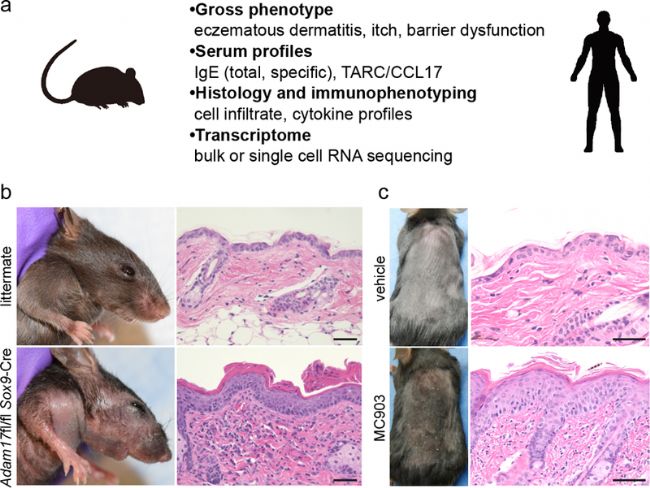 Fig3. Examples of AD mouse models[3].
Fig3. Examples of AD mouse models[3].
05 特应性皮炎小鼠模型的特点
★ 与人相似,具有红斑、瘙痒、干燥等症状;
★ 遗传背景清晰,实验结果可靠稳定;
★ 易于操作和观察;
★ 有利于降低研发过程中的成本与难度。
06 特应性皮炎小鼠模型的应用
★ 帮助揭示特应性皮炎的发病机制和免疫途径;
★ 用于测试和评估新的治疗方法和药物;
★ 研究环境因素对特应性皮炎的影响;
★ 为寻找预防策略提供重要线索。
南模生物自主研发了OXA(Oxazolone)诱导的特应性皮炎(Atopic Dermatitis, AD)动物模型。该模型选择通常选择BALB/c小鼠或C57BL/6小鼠,将OXA溶液涂抹在小鼠耳朵或背部皮肤上,连续数天,以致敏动物,此后重复涂抹OXA溶液以激发动物皮肤炎症反应。
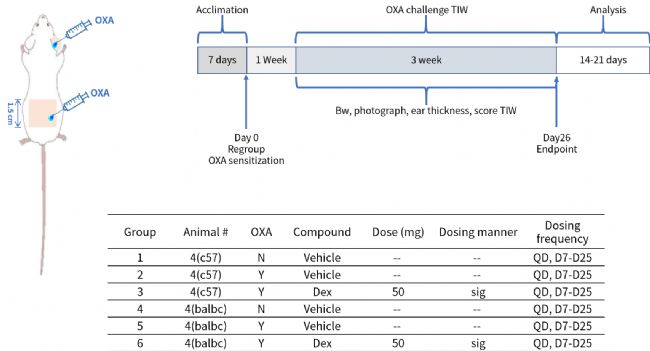
该小鼠模型可出现类似人类AD的症状:如皮肤红斑、丘疹、渗出、鳞屑和增厚等,伴有显著的搔抓行为。
皮肤组织学检查显示表皮增厚、角质形成细胞增生、真皮炎性细胞浸润等特点。局部和全身性Th2细胞介导的免疫反应增强,IgE水平升高,类似于人类AD的免疫特征[6-7]。
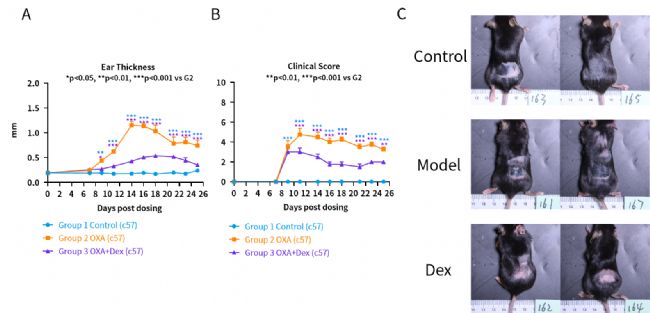
OXA induced increasing of ear thickness and clinical score (erythema, skin thickness and scabby) while Dex can relieve these symptoms. (A) ear thickness (B) clinical score of skin (C) gross observation on Day 21
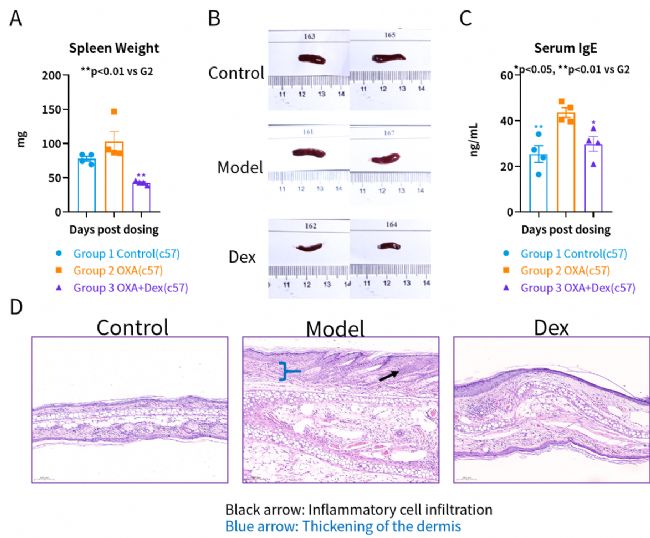
OXA motivated immune system. (A) spleen weight (B) spleen photo (C) serum IgE (D) Mice ear HE pathology
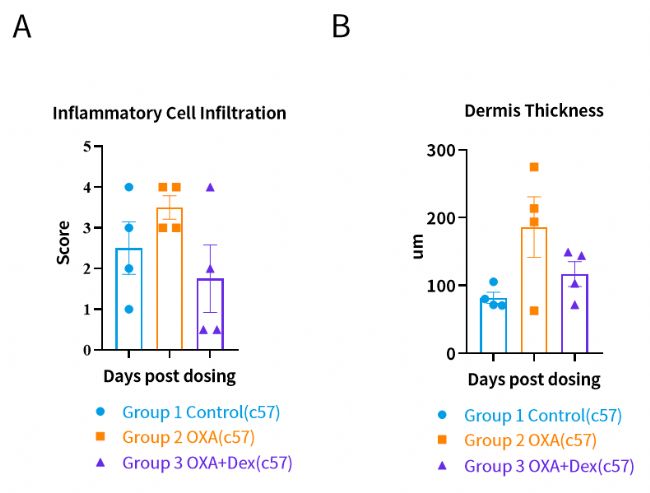
Mice pathology score. (A) inflammatory cell infiltration (B) dermis thickness

OXA induced increasing of ear thickness and clinical score (erythema, skin thickness and scabby) while Dex can relieve these symptoms. (A) ear thickness (B) clinical score of skin (C) gross observation on Day 21
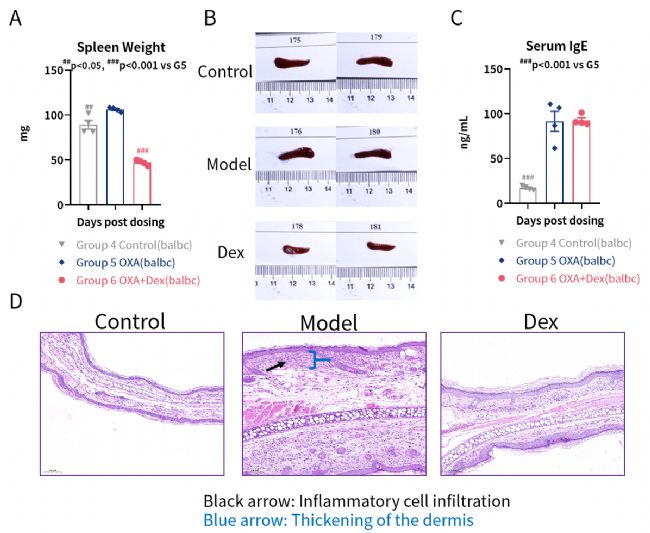
OXA motivated immune system. (A) spleen weight (B) spleen photo (C) serum IgE (D) Mice ear HE pathology. Black arrow: Inflammatory cell infiltration
Blue arrow: Thickening of the dermis

Mice pathology score. (A) inflammatory cell infiltration (B) dermis thickness
该模型可用于评估新药和治疗方法的有效性,为AD治疗提供实验依据。但需注意,动物模型与人类疾病仍存在差异,研究结果需谨慎解读。
参考文献
1. Schuler CF 4th, et al. Novel insights into atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 May;151(5):1145-1154.
2. Kim D, Kobayashi T, Nagao K. Research Techniques Made Simple: Mouse Models of Atopic Dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019 May;139(5):984-990.e1.
3. Kim J, Kim BE, Leung DYM. Pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis: Clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019 Mar 1;40(2):84-92.
4. Weidinger, S., & Novak, N. (2016). "Atopic dermatitis." The Lancet, 387(10023), 1109-1122.
5. Boguniewicz, M., & Leung, D. Y. M. (2011). "Atopic dermatitis: a disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation." Immunological Reviews, 242(1), 233-246.
6. Man, M. Q., Hatano, Y., & Elias, P. M. (2008). "Characterization of a hapten-induced murine model of atopic dermatitis showing a shift from acute to chronic dermatitis." Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 128(3), 381-389.
7. Kobayashi, T., & Amagai, M. (2020). "Epidermal barrier dysfunction and its role in atopic dermatitis." Experimental Dermatology, 29(3), 172-181.
关于我们
上海南方模式生物科技股份有限公司(Shanghai Model Organisms Center, Inc.,简称"南模生物"),成立于2000年9月,是一家上交所科创板上市高科技生物公司(股票代码:688265),始终以编辑基因、解码生命为己任,专注于模式生物领域,打造了以基因修饰动物模型研发为核心,涵盖多物种模型构建、饲养繁育、表型分析、药物临床前评价等多个技术平台,致力于为全球高校、科研院所、制药企业等客户提供全方位、一体化的基因修饰动物模型产品解决方案。





