|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [发表评论] [本类其他产品] [本类其他供应商] [收藏] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 销售商: 上海玉研科学仪器有限公司 | 查看该公司所有产品 >> |
玉研仪器自主研发脑立体定位仪十四年,适用于大鼠、小鼠等实验动物,经典十字操作臂实现精准定位,精度可达10微米,特制螺纹精密螺杆,稳固不晃动实现对特定脑区的精确定位,是神经环路研究、神经系统性疾病、神经药理等领域内的重要研究设备,广泛面向全国各大科研院校,医院,高新企业,药企,医疗机构等科研单位。
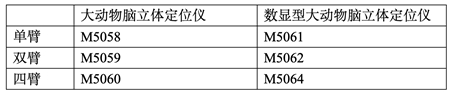
大动物脑立体定位仪(大动物双臂脑立体定位仪,大动物单臂脑立体定位仪,大动物数显型脑立体定位仪)

型号:M5059
根据需求不同,有多种不同的型号可供选择:大动物经典机械型,大动物数显型,数控型,双臂型,四臂型,敬请来电咨询。
1. 定位角度灵活多样
2. 激光刻度,清晰易读
3. 定位准确,稳定
4. 价格合理
主要构造:
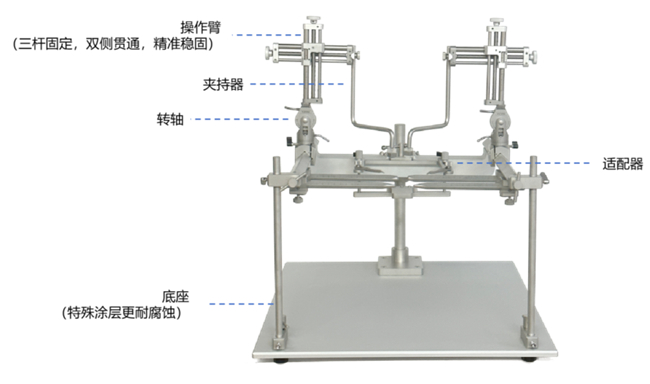
是一种非常高效的固定大动物脑部的仪器。最多可以在两个平行轨道上安装六个操作臂,可以实现在一个动物上多个探针独立定位。
锁定可靠
在进行大动物脑立体定位操作时,有时会需要从动物的侧面或是下面来进行操作,这时就需要将操作臂倾斜一定角度,可靠的锁定对于这种操作来说非常的重要。
全方位调节
通过引导螺纹,操作臂可以控制左右和上下方向的移动,前后控制通过楔形榫头来进行,在每个方向上都可以移动80mm。通用关节则使操作者可以在上下或左右平面上,让夹持器的最大转动可达90度。改进型的锁定部件可以让脑立体定位仪锁定在任何角度而不发生滑动,当然也提供了90度垂直方向的绝对锁定。
多功能
其它型号的动物适配器和耳棒都可以用到51800型大动物脑立体定位仪上。
移动平滑
标准型脑立体定位仪采用三线螺纹,可实现很好的位置定位,定位过程平滑,线性。
可选前后微调组件
可选的51858组件,可以25mm范围内,以10微米为步进,前后微调。通过一个伸出的旋纽来控制导轨和操作避的前后移动。
根据需要,有多种配置和型号可供选择
动物脑立体定位仪部分参考文献:
1. Albéri, L., Lintas, A., Kretz, R., Schwaller, B., & Villa, A. E. (2013). The calcium-binding protein parvalbumin modulates the firing 1 properties of the reticular thalamic nucleus bursting neurons. Journal of neurophysiology, 109(11), 2827-2841.
2. Sonati, T., Reimann, R. R., Falsig, J., Baral, P. K., O’Connor, T., Hornemann, S., Aguzzi, A. (2013). The toxicity of antiprion antibodies is mediated by the flexible tail of the prion protein. Nature, 501(7465), 102-106.
3. Ali, I., O’Brien, P., Kumar, G., Zheng, T., Jones, N. C., Pinault, D., O’Brien, T. J. (2013). Enduring Effects of Early Life Stress on Firing Patterns of Hippocampal and Thalamocortical Neurons in Rats: Implications for Limbic Epilepsy. PLOS ONE, 8(6), e66962.
4. Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., & McQuiston, A. R. (2013). Synaptic Muscarinic Response Types in Hippocampal CA1 Interneurons Depend on Different Levels of Presynaptic Activity and Different Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes. Neuropharmacology.
5. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
6. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
7. Babaei, P., Tehrani, B. S., & Alizadeh, A. (2013). Effect of BDNF and adipose derived stem cells transplantation on cognitive deficit in Alzheimer model of rats. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3, 156-161.
8. Gilmartin, M. R., Miyawaki, H., Helmstetter, F. J., & Diba, K. (2013). Prefrontal Activity Links Nonoverlapping Events in Memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(26), 10910-10914.
9. Feng, L., Sametsky, E. A., Gusev, A. G., & Uteshev, V. V. (2012). Responsiveness to nicotine of neurons of the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract correlates with the neuronal projection target. Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(7), 1884-1894.
10. Clarner, T., Diederichs, F., Berger, K., Denecke, B., Gan, L., Van der Valk, P., Kipp, M. (2012). Myelin debris regulates inflammatory responses in an experimental demyelination animal model and multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia, 60(10), 1468-1480.
11. Girardet, C., Bonnet, M. S., Jdir, R., Sadoud, M., Thirion, S., Tardivel, C., Troadec, J. D. (2011). Central inflammation and sickness-like behavior induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol: A PGE2-independent mechanism.Toxicological Sciences, 124(1), 179-191.
12. Hruška-Plocháň, M., Juhas, S., Juhasova, J., Galik, J., Miyanohara, A., Marsala, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A27 Expression of the human mutant huntingtin in minipig striatum induced formation of EM48+ inclusions in the neuronal nuclei, cytoplasm and processes. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
13. Brooks, S., Jones, L., & Dunnett, S. B. (2010). A29 Frontostriatal pathology in the (C57BL/6J) YAC128 mouse uncovered by the operant delayed alternation task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A10.
14. Yu, L., Metzger, S., Clemens, L. E., Ehrismann, J., Ott, T., Gu, X., Nguyen, H. P. (2010). A28 Accumulation and aggregation of human mutant huntingtin and neuron atrophy in BAC-HD transgenic rat. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
15. Baxa, M., Juhas, S., Pavlok, A., Vodicka, P., Juhasova, J., Hruška-Plocháň, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A26 Transgenic miniature pig as an animal model for Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A8-A9.
专业的售后服务队伍
在保修期内,凡非人为因素导致仪器的故障均免费维护,售后服务中心将为用户免费更换配件,不收取任何费用,仪器保修期为:1年





